
However, git fetch is safer and more flexible, while git pull is faster and more convenient. In summary, git fetch and git pull are both useful Git commands for downloading changes made to a remote repository. This means that git fetch is useful for syncing changes made to the remote repository with your local repository, while git pull is useful for integrating changes made to the remote branch with your local branch. Den wuz w'en he git er settin ' - down, he ain't nowise a - lookin ' foh.
#Git fetch origin code#
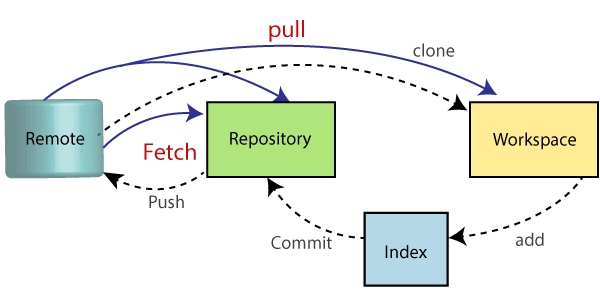
This means that git fetch is safer than git pull, as it allows you to review changes before merging them into your code base.Īnother difference is that git fetch updates your local repository's remote tracking branches, while git pull updates your local branch with the changes from the remote branch. Hiller would explain the origin of the book. The key difference between git fetch and git pull is that git fetch only downloads changes made to the remote repository, while git pull downloads and merges changes into your working directory. This command downloads any new changes made to the remote repository and merges them into your working directory. In this example, origin is the name of the remote repository you are pulling changes from, and main is the name of the branch you are pulling changes from.
#Git fetch origin how to#
Here is an example of how to use git pull $ git pull origin main This means that any changes made to the remote repository will be reflected in your codebase. The git pull command downloads changes made to the remote repository and immediately merges them into your working directory. As the fetched commits are saved as remote branches and not integrated into our. What this will do is remove references to remote branches in the folder. This command downloads any new changes made to the remote repository and updates your local repository's remote tracking branches. To view the remote branches that was fetched we use the git branch -r command. In this example, origin is the name of the remote repository you are fetching changes from. Here is an example of how to use git fetch: $ git fetch origin This means that the changes are not immediately visible in your codebase, but are stored in your local repository's remote tracking branches.

The git fetch command downloads changes made to the remote repository to your local repository, without merging them into your working directory. While both commands download changes from a remote repository, there are some key differences between them. Two of the most commonly used Git commands are git fetch and git pull. Git is a powerful version control system that allows developers to manage changes made to their codebase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
